# rust 二叉树构建
定义解构:
// 定义 TreeNode 解构 | |
pub struct TreeNode{ | |
pub val: i32, | |
pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, | |
pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, | |
} | |
// Option<T> 是一个枚举类型,它可以包含 Some (T) 表示有值,或者 None 表示没有值。 | |
// Rc<T> 是引用计数(Reference Counting)智能指针,用于多所有权的数据结构。在这里,它用于创建树节点的左右子树。 | |
// RefCell<T> 是一个提供内部可变性的类型,它允许在运行时检测借用规则。在这里,它用于 Rc 中,以允许在 Rc 的内部进行可变操作。 |
定义 TreeNode 方法:
impl TreeNode{ | |
//new 方法获得类型 | |
pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self{ | |
TreeNode{ | |
val, | |
left: None, | |
right: None, | |
} | |
} | |
// 构建二叉树方法 | |
pub fn insert(&mut self, val: i32) ->(){ | |
if val < self.val { | |
if let Some(left) = &self.left { | |
left.as_ref().borrow_mut().insert(val); | |
} else{ | |
self.left = Some(Rc::new(ReCell::new(TreeNode::new(val)))); | |
} | |
}else{ | |
if let Some(right) = &self.right { | |
right.as_ref().borrow_mut().insert(val); | |
}else { | |
self.right = Some(Rc::new(RefCell::new(TreeNode::new(val))); | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
} |
TreeNode 遍历方法:
impl TreeNode{ | |
// 前:根左右 中:左根右 后:左右根 | |
// 基于 Self 方法的前、中、后续遍历 TreeNode. 方法名 () | |
pub fn front_order(&self){ // 这里并不要 mut 遍历只读,mut 难度更大 | |
println!("{}",self.val); | |
if let Some(node) = &self.left{ // 这里去掉了 Option 和 Rf | |
node.borrow_mut().front_order();// 去掉 ReCall | |
} | |
if let Some(node) = &self.right{ | |
node.borrow_mut().front_order(); | |
} | |
} | |
pub fn in_order(&self){ | |
if let Some(node) = &self.left{ | |
node.borrow_mut().in_order(); | |
} | |
println!("{}",self.val); | |
if let Some(node) = &self.right{ | |
node.borrow_mut().in_order(); | |
} | |
} | |
pub fn back_order(&self){ | |
if let Some(node) = &self.left{ | |
node.borrow_mut().back_order(); | |
} | |
if let Some(node) = &self.right{ | |
node.borrow_mut().back_order(); | |
} | |
println!("{}",self.val); | |
} | |
// 如果这个要改为 & amp;mut self 请将 node.borrow_mut. 方法 () 替换为 node.as_ref ().borrow_mut (). 方法 (); 注意 borrow 和 borrow_mut 的区别 | |
// pub fn in_order(&mut self){ | |
// if let Some(ref node) = &self.left { // | |
// node.as_ref().borrow_mut().in_order(); | |
// } | |
// if self.val == 36 { | |
// self.val = 100; | |
// } | |
// println!("{}", self.val); | |
// if let Some(ref node) = &self.right { | |
// node.as_ref().borrow_mut().in_order(); | |
// } | |
// } | |
// 基于函数的前、中、后续遍历 fn 参数不是 self | |
pub fn frontorder(node: &mut Option<Rf<RefCell<TreeNode>>>){ | |
if let Some(node) = node{ | |
println!("{}",node.borrow().val); | |
TreeNode::frontorder(node.as_ref().borrow_mut().left.borrow_mut()); | |
TreeNode::frontorder(node.as_ref().borrow_mut().right.borrow_mut()); | |
} | |
} | |
pub fn inorder(node: &mut Option<Rf<RefCell<TreeNode>>>){ | |
if let Some(node) = node{ | |
TreeNode::inorder(node.as_ref().borrow_mut().left.borrow_mut()); | |
println!("{}",node.borrow().val); | |
TreeNode::inorder(node.as_ref().borrow_mut().right.borrow_mut()); | |
} | |
} | |
pub fn backorder(node: &mut Option<Rf<RefCell<TreeNode>>>){ | |
if let Some(node) = node{ | |
TreeNode::backorder(node.as_ref().borrow_mut().left.borrow_mut()); | |
println!("{}",node.borrow().val); | |
TreeNode::backorder(node.as_ref().borrow_mut().right.borrow_mut()); | |
} | |
} | |
} |
主函数:
use std::borrow::BorrowMut; | |
fn main() { | |
let aa = Vec::from([4,1,6,0,2,5,7,3,8]); | |
let mut i=0; | |
let mut root = Some(Rc::new(RefCell::new(TreeNode::new(aa[i])))); | |
i+=1; | |
while i <aa.len(){ | |
if let Some(ref root1) = root { | |
root1.as_ref().borrow_mut().insert(aa[i]); | |
} | |
i+=1; | |
} | |
// root.as_ref().unwrap().as_ref().borrow_mut().insert(3); | |
// root.as_ref().unwrap().as_ref().borrow_mut().insert(7); | |
// root.as_ref().unwrap().as_ref().borrow_mut().insert(2); | |
// root.as_ref().unwrap().as_ref().borrow_mut().insert(4); | |
// root.as_ref().unwrap().as_ref().borrow_mut().insert(1); | |
// println!("{:?}",root); | |
println!("--------------------------------------", ); | |
let mut hh = Solution::bst_to_gst(root); | |
println!("{:?}", hh); | |
TreeNode::inorder_traversal(hh.as_ref()); | |
println!("back-------", ); | |
TreeNode::backorder_traversal(root.as_ref()); | |
println!("front-------", ); | |
TreeNode::frontorder_traversal(root.as_ref()); | |
println!("--------------------------------------", ); | |
// TreeNode::bt_backorder_traversal(root.as_ref()); | |
// println!("--------------------------------------", ); | |
// println!("in-------", ); | |
root.as_ref().unwrap().as_ref().borrow_mut().in_order(); | |
// println!("back-------", ); | |
root.as_ref().unwrap().as_ref().borrow_mut().back_order(); | |
// println!("front-------", ); | |
root.as_ref().unwrap().as_ref().borrow_mut().front_order(); | |
} |
# 练手题目 leet1038:
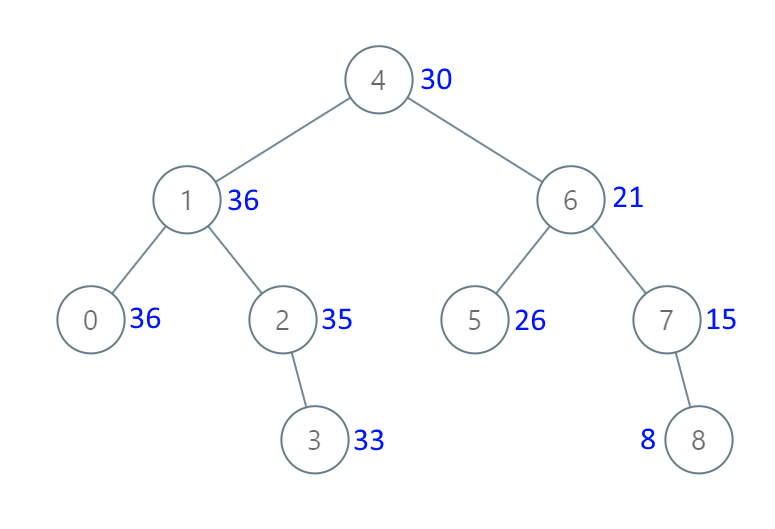
思路:首先确定遍历顺序,这里不是更像是将 中序遍历(左根右),修改为另一种(右根左),然后累加,返回 total 值即可,所以这里首先确定使用 mut Option<Rf<RefCell <TreeNode> >> 作为参数,代码如下:
use std::rc::Rc; | |
use std::cell::RefCell; | |
use std::borrow::BorrowMut; | |
impl Solution { | |
pub fn bst_to_gst(mut root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> { | |
Self::bt_backorder_traversal(&mut root,0); | |
root | |
} | |
pub fn bt_backorder_traversal(node: &mut Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, mut total : i32) -> i32 { | |
if let Some(node) = node { | |
total=Self::bt_backorder_traversal(node.as_ref().borrow_mut().right.borrow_mut(), total); | |
total+=node.borrow().val.clone(); | |
node.as_ref().borrow_mut().val=total; | |
total=Self::bt_backorder_traversal(node.as_ref().borrow_mut().left.borrow_mut(),total); | |
} | |
total | |
} | |
} |